Why Does the Sky Turn Red at Sunrise and Sunset?
An orange or red Sun in the early morning or late evening is a sight to behold. The sky takes on these vivid hues due to a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering.
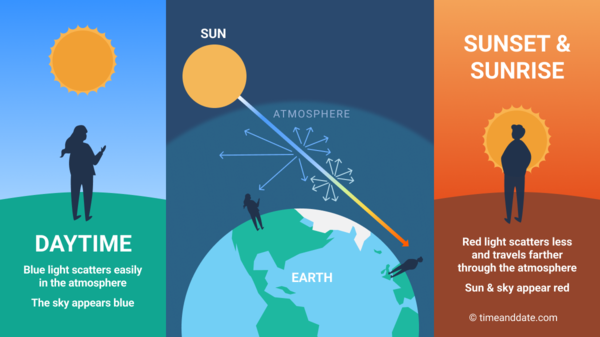
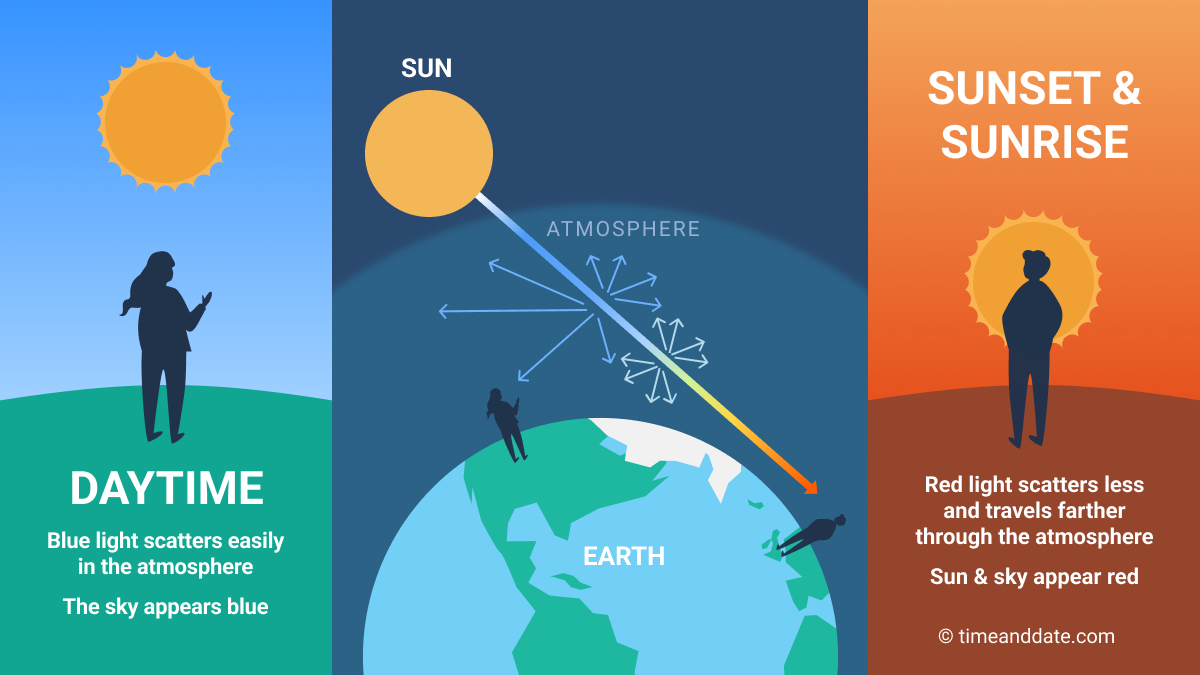
Blue light scatters easily in the atmosphere so the daytime sky appears blue. When the Sun is low in the sky, sunlight has to travel farther through the atmosphere, the blue light is scattered away, and the sky and Sun appear red.
©timeanddate.com
The moments when 99% of people see sunlight
Made of Different Colors
The sunlight that we see is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by the Sun. Known as the visible light, it looks white but is composed of colors of different wavelengths, with violet having the shortest wavelength and red having the longest. You can see the different colors when you look through a prism or when a rainbow appears in the sky.
Earth’s Atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily made up of gas molecules, with oxygen comprising about 21% and nitrogen about 78%. In addition, water molecules in the form of droplets, ice crystals, and vapor, and particles such as dust, pollutants, and ash can be found in the atmosphere, which is denser closer to the Earth and thins out as the altitude increases.

The Sun's rays have to travel a shorter path through Earth's atmosphere in the day. This is why the sky looks blue during the day.
©iStockphoto.com/bluejayphoto
Blue Skies And Yellow Sun
When sunlight strikes gas molecules, such as nitrogen and oxygen, light of longer wavelengths, like red, yellow, and orange, easily passes through, while light of shorter wavelengths, such as blue and violet, is absorbed and then scattered in all directions by the gas molecules.
When you look up at the sky during the day, this scattered blue and violet light reaches your eyes, however, the human eye is more receptive to blue frequencies than violet frequencies, so the sky looks blue.
This phenomenon is known as Rayleigh scattering. It is named after British physicist John William Strutt, also known as Lord Rayleigh. Besides making the sky look blue, it is also the reason why the Sun looks yellow during the day even though sunlight is white. When the Sun is high in the sky, the light has to travel a shorter distance through the atmosphere. This means most of the yellow, orange, and red light passes through while a small amount of blue and purple light is scattered and removed from the mix. The Sun, therefore, looks yellow for us here on Earth.
Longer Distance to Travel
During sunsets and sunrises, when the Sun is closer to the horizon, sunlight has to travel through a longer distance and more of the dense environment to reach an observer’s eye.
Sunrise and sunset times in your city
Due to Rayleigh scattering, most of the light of shorter wavelengths – the blue, violet, and green – are scattered away multiple times, leaving only lights of longer wavelength – the red, orange, and yellow – to pass straight through to the observer.
This is why a rising and setting Sun tends to take on spectacular hues of red, orange, and yellow.

Dust and pollution can reduce the vibrancy of sunrise and sunsets.
©iStockphoto.com/dansolomonphoto
Dust and Pollution
The quality of the air that sunlight has to pass through also has an effect on the color of sunrises and sunsets. Dust particles and pollutants tend to tone down the colors in the sky as well as impede light from reaching the observer on the ground. Because of this, the sky takes on dull hues of red and yellow when the air is full of dust and pollutants. This is why sunrises and sunsets in rural areas, over the ocean, and deserts are much more vibrant and colorful than over cities and urban areas.
Tips: Take pictures of sunrises and sunsets
Red Moon
Rayleigh scattering is also responsible for giving the Moon a reddish or orange hue during total lunar eclipses. The condition of the Earth's atmosphere, including the amount of pollution and dust from storms and volcanic eruptions, can affect the shade of red the Moon takes on during the eclipse.